Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)
Endoscopic Ultrasonography [EUS] is an imaging technique that combines endoscopy with ultrasonography. EUS is performed using an endoscope with a small ultrasound mechine attached to the tip of the endoscope. The endoultrasound probe is passed through the mouth or anus to the area to be examined under endoscopic view. The ultrasound component is then utilized to examine the walls and the surrounding structures of the upper and lower gastrointestinal tract. The esophagus, stomach, duodenum and the rectum are the organs which are studied by this equipment. EUS is also used to study internal organs that lie next to the gastrointestinal tract, such as the mediastinum, gallbladder, biliary tract and the pancreas.
There are two types of EUS probes each one of them having specific applications.
Radial Probe
The radial probe is a diagnostic scope with a view similar to the view obtained in CT scan. It is equipped with a high frequency probe which gives high clarity images of objects closer to the probe. There is no radiation because this technology uses only sound waves. Objects as small as 2mm can be seen separately.
Linear Probe
The linear probe gives images of smaller area and hence should be rotated to get to the required position. This scope is provided with an additional facility enabling the specialist to pass needles and other accessories into the sorrounding tissues under full ultrasound guided visualization. There is a doppler scanning mechanism that helps avoid blood vessels during the puncture. The needle is used for aspiration of tissues and fluid for cytology (FNAC) examination. This scope is also called a therapeutic scope because it is used for various treatment purposes.
Applications of EUS
- EUS provides detailed images of the anatomy of the digestive tract.
- EUS can be performed to further evaluate the pancreas when abnormalities are noted on CT or conventional abdominal ultrasonography.
- EUS can also be performed to evaluate abnormal areas in the esophagus, stomach and duodenum noted on either endoscopy or an X-ray examination.
- EUS is the only investigation which shows the gastrointestinal wall as a layered structure as seen in microscopic examination of tissues. This feature is helpful understand the exact nature of the pathology.
Applications of EUS in patients with cancer
- EUS can help determine the extent of certain malignancies of the gastrointestinal tract. These include cancer of the esophagus, pancreas, stomach, and rectum. EUS provides information as to the depth of involvement of the cancer.
- EUS shows if malignant cells have invaded the walls of the GI tract or whether malignancy has spread to adjacent lymph nodes or nearby vital structures such as major blood vessels.
- EUS is the only investigation which can identify lymph nodes smaller than 1cm. Together with a fine needle aspiration, EUS can be a valuable tool in the diagnosis and accurate staging of cancer spread and to guide in the proper treatment of cancers. EUS can help determine the need for or avoidance of surgical procedures.
- Together with fine needle aspiration, EUS can be a valuable tool in the diagnosis and accurate staging of lung cancer. EUS helps to differentiate a malignant lymph node from a tuberculous lymphnode particularly in the mediastinum.
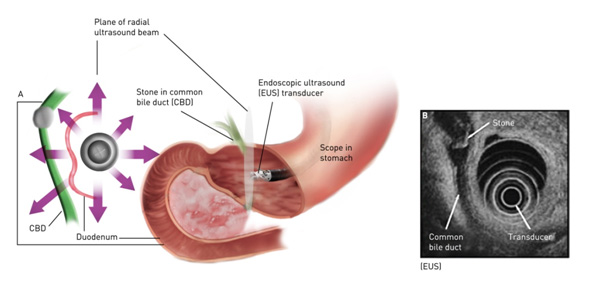
Applications of EUS in evaluation of the Common bile duct
- EUS is a very useful tool to evaluate the CBD. Abnormalities like tumours, stones and dilataton of CBD can be detected.
- Microlithiasis in CBD and gallbladder can be detected and EUS is the only test which detects microlithiasis. Microlithiasis of the gallbladder is an important cause of biliary pancreatitis.
EUS for management of pseudocyst of pancreas
EUS is the most appropriate treatment of choice for the drainage of pseudocyst of pancreas. EUS can clearly show the type of cyst, its contents and also whether there is any blood vessel on the needle track during the puncture. It is possible to deploy stent inside the cyst from the stomach.